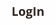FEATURES
Fully Integrated
Connects directly into all areas
of CAPITAL Business Manager
where applicable.
Assemblies
Assemblies are production
‘entities’ made up of all or
some of the following
elements:
•
a bill of materials
•
a finished items list
•
a work order
•
labour time
•
expenses, auxiliary costs
and/or ‘out plant’
•
notes
•
linked documents
•
routings (manufacturing
steps)
Assembly Templates
An assembly may be set-up as
a template that is easily copied
into a production assembly
that can then be assigned to a
production process.
Sales Orders
Sales orders can automatically
trigger the creation of
production orders.
Flexible Scheduling
The Master Production
Schedule (MPS) is graphically
visualised and easily modified.
Manufactured Items
Database
Manufactured Items are
tracked by:
•
Where it is being
manufactured
•
Where it is found on all bills
of materials
•
Next scheduled build date
•
Last build date
•
First build date
•
last amended date
•
Last sold date
•
Last forecast (requirement)
date.
•
Estimated monthly demand
Build Metrics
Automatic tracking of
scheduled date, completion
dates and variances from
completion date. As well as
estimated capacity versus
actual capacity and variance.
Reverse Build
Easily undo a built assembly
by pressing the ‘Reverse’
button.
Automated Replenishment
Automatic generation of
‘reorder plans’ that are based
on scheduled production
orders and lead times.
Purchase Orders
View all open purchase orders
relating to components of an
assembly.
Partial Build
Assembly runs may be part
built and the production run
for an assembly completed at
a later stage.
Non-Diminishing Stock
Non-diminishing items may be
included in manufacturing and
separately costed.
Negative Productiion
Assign negative stock to
material lists so long as the
stock item is not a kit and the
total value of the materials list
is not less than zero. For
example, when producing X
you are left with subsidiary
products A, B and C, that may
be used for other purposes or
placed back into inventory.
Cost Estimating
Assign estimated materials
costs and later compare to
actual costs.
Cost may also be apportioned
by percentage or fixed fixed
dollar value. The total of your
finished cost dollar values
must add up to the total of
your labour, materials and
expense inputs, however.

Capital Office Business Software

Business Software You Won’t Outgrow

© 1985-2026 CAPITAL Office Business Software
CAPITAL Manufacturing makes a complex subject as easy as possible by providing state of the art tools designed
from the ground up with a strong emphasis on visual guidance using clearly designed dynamic lists and graphs.
Production Planning (PP)
The Production Plan is a consolidated manufacturing item list, showing what is scheduled for production over a specified date range. It is the plan for future production. The production plan also shows: • The dollar value cost of production per scheduled manufactured item • The number of units scheduled for production • Customer order requirements • A forecast of requirements over each time period • A projected stock on hand quantity for the time period The production plan will also show open assemblies (bills of material in production) that have not yet been scheduled but that you will need to schedule.Master Production
Scheduling (MPS)
The Master Production Schedule (MPS) allows you to organise the sequence in which assemblies are produced and to assess your materials (stock), labour and capacity requirements. All assemblies with a stage setting of 'open' initially appear on the schedule. Open assemblies are unscheduled so appear at the bottom of the schedule. Once a proposed or actual production date is assigned to an assembly - this is referred to as the schedule date - it is assigned its appropriate place within the schedule.Manufactured Products Database
Manufactured Products is the list of all products assembled or produced by your business. Manufactured products also have a matching product found in stock control. Manufactured products are produced when the Assembly Manager builds assemblies.Finite Capacity Scheduling (CRP)
The Finite Capacity Scheduler will automatically perform the challenging task of assigning (or changing) scheduling dates for assemblies found on the production schedule, and update these as well as update your Production Plan. The Finite Capacity Scheduler does not alter the scheduling dates of assemblies set to the stage of 'Committed' or 'In Progress' or assemblies that have had their scheduling dates locked. The assemblies found on the Master Production Schedule will be scheduled based on the constraints specified when running the Capacity Wizard. Scheduled assemblies are always assigned a Stage setting of 'Proposed'. Assemblies that are locked, or have a stage setting of 'Committed' or 'In Progress' are never rescheduled. If a schedule date cannot be found within the constraints specified, the assembly will not be scheduled. This may result in an assembly that was previously scheduled becoming unscheduled, unless that assembly has its schedule date locked. Assemblies are first sorted by order or required dates, priority, and other criteria. If an assembly has a required date and you have selected to schedule by customer requirement date, these assemblies will be scheduled first. The Finite Capacity Scheduler will attempt to fit them into the schedule at a date prior to the required date that allows sufficient time to manufacture the assembly. This could result in assemblies without required dates being scheduled before assemblies with required dates. A scheduled assembly is subject to the following constraints: • Available resource capacity such as labour time. • Any missing components or raw materials can be acquired before manufacturing begins. This time window is determined by lead time. The determination is based on worst case: which would be a component or raw material that is not available to be drawn from stock, and which has the longest lead time for acquisition.Manufacturing Demand Forecasting
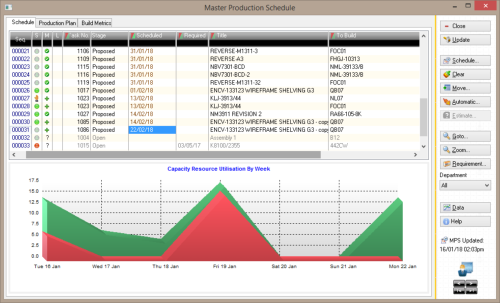
Manufacturing Demand Forecasting allows you to forecast demand for your manufactured goods using a variety of statistical methods such as: • Best Fit • Simple Historical Average • Weighted Historical Average • Simple Trend Selecting ‘Best Fit’ tells Demand Forecasting to test your historical data against available forecasting techniques. The most accurate forecasting method, based on available data, is then automatically assigned to your manufactured item.Material Resource Planning (MRP)
Material Resource Planning (MRP) refers to the process of ensuring you have on hand the required materials such as components or raw materials, to complete your production task. Core elements of resource planning involve: • Ascertaining what materials or components you have in stock and what requires acquisition. Each stock assembly may reference one or more bills of materials or product component or raw material lists from which this information is obtained. • Analysing material lead times to inform you as to when materials you do not have will need to be ordered. (Sometimes referred to as JIT or ‘just in time’.) • Lead times are related back to the assembly schedule date, which is the planned production date.Material Resource Planning (MRP2)


•
Exponential Smoothing
•
Seasonality
•
Seasonality with Trend